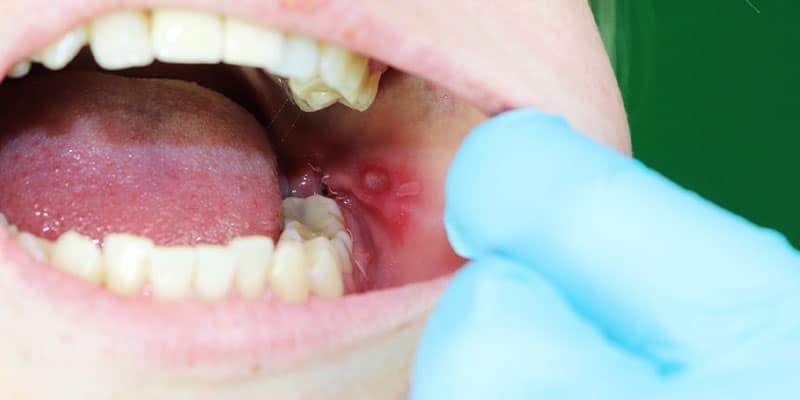
Canker sores are tiny, thin sores in the mouth. Dentist in Houston, TX explains that you might acquire them on the inside of your lips or cheeks, at the base of your gums, or beneath your tongue. Canker sores are also known as aphthous ulcers. Canker sores vary from cold sores (also known as fever blisters). Cold sores typically appear on the outside of your lips or in the corners of your mouth.
Treatment of Canker Sores
There are several home treatments and over-the-counter drugs that can help you recuperate faster. If you have canker sores that do not go away, your dentist or doctor may recommend stronger prescription medicine. Here are the treatment options for canker sores:
- Mouth rinse: Rinsing with salt water can alleviate discomfort and lower the risk of infection. Make a saltwater rinse by combining one teaspoon of salt and one cup of water. Take a mouthful of the drink and keep it in your mouth for two minutes to cover the afflicted region before spitting it out. Do not consume it. Repeat the method four times every day.
- Milk of Magnesia: Similar to salt, milk of Magnesia helps remove acids from the mouth. Apply a tiny quantity to the canker sore using a cotton pad a few times daily. Milk of magnesia has also been proven to reduce pain and speed up the healing process.
- Over-the-counter medicine: Purchase an over-the-counter numbing medication, such as Orabase, to use on your canker sores. Use a cotton swab to administer the medication. Apply it on your sores 3-4 times each day. Consult your doctor before administering mouth-numbing medication to children of any age.
- Pain relievers: Take pain killers such aspirin (Bayer), ibuprofen (Advil), or naproxen (Aleve). Aspirin should not be given to anybody under the age of 18 due to the danger of Reye syndrome. Take precautions when using medications.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics such as Doxycycline mouthwash may be beneficial in the treatment of recurring canker sores. Low-dose oral doxycycline can also be given as tablets. Prolonged antibiotic treatment for canker sores may result in oral thrush or mouth candidiasis as a consequence. If the canker sores are severe and untreated, the bacterial infections may progress to more serious diseases such as cellulitis or Ludwig’s angina.
In extreme situations, prescriptions for fluocinonide gel (Lidex) or chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash may be issued.